Home

Orchidopexy: All You Need to Know About Its Procedure, Risks, and Recovery
In this Article

Getting Pregnant
Orchidopexy: All You Need to Know About Its Procedure, Risks, and Recovery
Updated on 9 June 2023
Orchidopexy, orchiopexy, or testicular fixation surgery, is a medical intervention designed to correct undescended testicles in males. It involves gently coaxing those shy testicles to descend into their rightful place within the scrotum. But what exactly happens during this procedure? What are the potential risks? And how long does it take to recover from orchidopexy surgery?
In this article, we will understand in detail orchidopexy meaning, how the surgery is carried out, what are the risks involved in it and how long the recovery can take.
Orchidopexy Meaning: What is it?
Orchidopexy meaning can be interpreted from its other name, testicular fixation surgery, a medical procedure performed to treat undescended testicles in males. In this procedure, the surgeon gently moves the testicles to the scrotum from their original position, usually in the abdomen or groin.
The aim is to properly position the testicles within the scrotum, allowing for normal development and function. Orchiopexy is a standard and effective treatment for undescended testicles, ensuring the overall health and well-being of the individual.
Why is Orchidopexy Performed?
Orchidopexy surgery is performed for the following reasons:
1. Undescended testicles
The primary reason for performing orchidopexy is to treat undescended testicles, where one or both testicles fail to descend into the scrotum properly.
2. Promote normal testicular development
Orchidopexy aims to position the undescended testicles into the scrotum to facilitate their average growth and development. This helps ensure proper hormone production and reproductive function.
3. Improve fertility potential
Correcting undescended testicles through orchidopexy can increase the chances of fertility in the future. Descending the testicles into the scrotum allows for optimal sperm production and maturation.
4. Reduce the risk of complications
Leaving undescended testicles untreated can lead to complications, including testicular torsion (twisting of the testicle), hernia, and an increased risk of testicular cancer. Orchidopexy reduces these risks and promotes long-term testicular health.
5. Enhance cosmetic appearance
Orchidopexy helps improve the cosmetic appearance of the scrotum by placing the testicles in their normal anatomical position. This can positively impact self-esteem and body image.
How is Orchidopexy Surgery Performed?
Orchidopexy surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves the following steps:
1. Incision
Depending on the specific case and surgical approach, the surgeon makes a small incision in the groin or scrotum.
2. Locating the testicle
The surgeon carefully locates the undescended testicle within the abdomen or groin area. In some cases, the testicle may be located just above the scrotum.
3. Mobilization
The testicle is carefully freed from any surrounding tissues or attachments. This allows the surgeon to manipulate and bring it down into the scrotum.
4. Securing the testicle
Once the testicle is brought into the scrotum, the surgeon ensures its proper placement and fixation. This may involve creating a small pouch in the scrotum and securing the testicle using sutures or other techniques.
5. Closure
The incision is then closed with sutures or surgical staples. The surgeon may also apply sterile dressings or adhesive strips to aid in the healing process.
The exact technique and approach may vary depending on factors such as the patient's age, the location of the undescended testicle, and the surgeon's preference. Orchiopexy is considered a safe and routine procedure with a high success rate in correctly positioning the testicle within the scrotum.
You may like : Testicular Ultrasound: What You Need to Know About the Procedure and Its Benefits
Risks and Complications of Orchidopexy
While orchidopexy is generally considered a safe procedure, like any surgical intervention, potential risks and complications are involved. These can include:
1. Bleeding
There is a risk of bleeding during or after the surgery. While rare, excessive bleeding may require additional medical intervention.
2. Infection
Infection at the surgical site is a potential complication. It is essential to keep the area clean and follow proper post-operative care instructions to minimize the risk of infection.
3. Testicular atrophy
In rare cases, the blood supply to the testicle may be compromised during surgery, leading to testicular atrophy (shrinkage). This can result in reduced fertility or hormonal imbalances.
4. Scrotal swelling and bruising
Swelling and bruising around the scrotum is common after orchidopexy. This usually resolves on its own within a few weeks, but it can cause discomfort during recovery.
5. Recurrence
Sometimes, the testicle may not remain appropriately positioned within the scrotum after orchidopexy. This may require additional procedures or interventions to correct the positioning.
6. Anesthesia risks
General anesthesia carries risks, including allergic reactions, breathing difficulties, and adverse reactions to medications. These risks are typically low but should be discussed with the anesthesiologist before the surgery.
Recovery and Aftercare for Orchidopexy
Recovery and aftercare following an orchidopexy surgery are essential for ensuring proper healing and optimal outcomes. Here are some important aspects to consider:
1. Rest and activity
It is important to take ample rest in the initial days after surgery. Avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sports for a few weeks, as your surgeon recommends. Gradually ease back into normal activities based on your doctor's instructions.
2. Pain management
After the surgery, you may experience some discomfort and pain in the scrotal area. Your doctor may prescribe pain medications to manage the pain. Follow the prescribed dosage and take any medications as directed.
3. Dressings and incision care
Keep the surgical area clean and dry. Your doctor may provide specific instructions on caring for the incision site and whether you need to change dressings. It's essential to follow these instructions to prevent infection.
4. Follow-up appointments
Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. These visits allow your doctor to monitor your healing progress, assess any potential complications, and address any concerns or questions you may have.
5. Supportive underwear
Wearing supportive underwear, such as briefs, during recovery can help provide comfort and minimize scrotum movement, promoting healing.
6. Hygiene
Maintain good hygiene by keeping the surgical area clean. Avoid soaking in baths, swimming pools, or hot tubs until your doctor gives you the green light.
7. Avoid straining
Straining during bowel movements can put pressure on the surgical area. To prevent this, maintain a diet high in fiber, drink plenty of water, and, if necessary, use stool softeners as your doctor recommends.
8. Follow dietary guidelines
Your surgeon may provide specific dietary guidelines to follow during the recovery period. Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in the healing process.
When to seek Medical Help after Orchidopexy
After undergoing an orchiopexy, it's essential to be aware of any signs or symptoms that may indicate a need for medical attention. While most patients recover well without complications, it's essential to promptly seek medical help if you experience any of the following:
1. Excessive bleeding
If you notice persistent or excessive bleeding from the surgical site that does not subside with pressure or affects your daily activities, seek medical help immediately.
2. Infection signs
Watch out for signs of infection, such as increasing pain, redness, swelling, warmth, or discharge from the incision site. Additionally, if you develop a fever, it could indicate an infection, and you should consult your healthcare provider.
3. Severe pain or discomfort
While some discomfort is expected after surgery, a healthcare professional should evaluate severe or worsening pain that is not relieved by pain medication.
4. Testicular changes
If you notice any changes in the size, shape, or consistency of the testicles, or if you experience severe swelling or bruising, it's essential to seek medical attention.
5. Recurrence of undescended testicle
In rare cases, the testicle that was surgically repositioned may not stay in place, and it may become undescended again. If you suspect this has occurred, consult your doctor for further evaluation.
6. Urinary problems
If you experience difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or other urinary issues, it is essential to seek medical help.
7. Allergic reactions
If you develop a severe allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or hives, seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, orchidopexy is a surgical procedure performed to correct undescended testicles. It is an essential intervention as it helps to improve fertility, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of testicular cancer. While orchidopexy surgery is considered safe and effective, knowing the potential risks and complications associated with the surgery is essential.
References
1. Elseth, A., & Hatley, R. M. (2021). Orchiopexy. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing.
2. Zouari, M., Dhaou, M. B., Jallouli, M., & Mhiri, R. (2015). Single scrotal-incision orchidopexy for palpable undescended testis in children. Arab Journal of Urology



Written by
Madhavi Gupta
Dr. Madhavi Gupta is an accomplished Ayurvedic doctor specializing in Medical content writing with an experience of over 10 years.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles
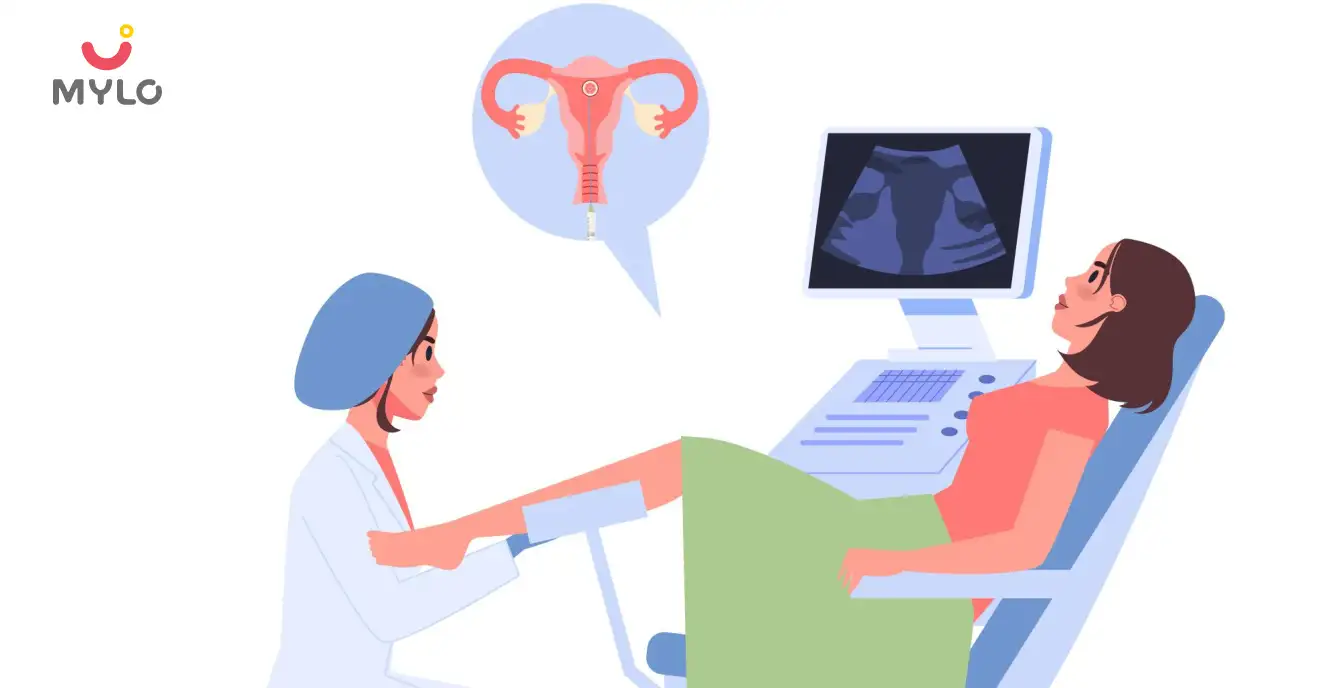

Reproductive health
Transvaginal Ultrasound: A Non-Invasive Tool for Early Detection of Reproductive Health Issues

Diet & Nutrition
New Mom Diet Plan – Month 11 Week 42
Male Infertility
Ejaculatory Duct Obstruction: How It Affects Male Fertility and What You Can Do About It
Testicular Ultrasound: What You Need to Know About the Procedure and Its Benefits

Symptoms of Low AMH to Watch Out For: A Health Alert for Women Trying to Conceive
Medical Procedures
Hysteroscopy: Everything You Need to Know About This Minimally Invasive Procedure
- Dalchini: How This Herb Can Make Way From Your Spice Rack to Your Medicine Cabinet
- Fenugreek Powder: Health Benefits of Fenugreek From Your Kitchen to Your Medicine Cabinet
- Moringa Powder: The Superfood You Need in Your Diet for a Healthy Lifestyle
- Genital Herpes: Causes, Symptoms, Risks & Treatment
- Ashokarishta: All You Need to Know About This Miracle Tonic for Women
- 10 Amazon Prime Movies to Look Forward to in 2023
- 10 Best Netflix Movies to Watch Out For in 2023
- Fertility Yoga: A Natural Solution to Boost Your Chances of Conception
- How to Get Regular Periods Naturally: Ayurvedic Herbs, Lifestyle Changes & Homeopathy
- Lodhra: The Wonder Herb for Women's Health
- Malabsorption Syndrome: Types, Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment
- Top 10 Short Bedtime Stories for Kids
- RH Incompatibility in Pregnancy - Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Symptoms & Treatment


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
Baby Carrier | Baby Soap | Baby Wipes | Stretch Marks Cream | Baby Cream | Baby Shampoo | Baby Massage Oil | Baby Hair Oil | Stretch Marks Oil | Baby Body Wash | Baby Powder | Baby Lotion | Diaper Rash Cream | Newborn Diapers | Teether | Baby Kajal | Baby Diapers Pants | Cloth Diapers | Laundry Detergent | Lactation Granules |








