Home

Scans & Tests

What to expect in a Nuchal Translucency scan during your Pregnancy?
In this Article

Scans & Tests
What to expect in a Nuchal Translucency scan during your Pregnancy?
Updated on 3 November 2023
Nuchal Translucency Scan- What does it indicate?
Are you pregnant? Then you will have scheduled appointments and screenings with the gynecologist till the baby is born. To identify any potential problems about the health of the unborn child and the mother, prenatal screenings are done by the doctor. Some of the problems that can be identified with such screenings are chromosomal abnormalities, gestational diabetes, or anemia.
Pregnancy screenings are usually conducted in the first, second, and third trimesters. The screening done during the first trimester gives the doctor early information about the health of the child and the risk for chromosome abnormalities.
NT scan report or the Nuchal Translucency scan enables the doctor to get an idea about such abnormalities. This kind of scan is usually done between 11 to 13 weeks of pregnancy. After this period, the tissue becomes thick and is no longer translucent. The results become inconclusive.
Why is an NT scan conducted?
NT scan is a popular screening test done during the first trimester. With the help of the NT scan report normal, the doctor can see the size of the clear tissue. This is also called the nuchal translucency and is located at the back of the neck of the baby.
It is not an unusual condition to have clear or fluid space at the back of the baby’s neck. However, if the child has too much clear space, it is indicative of Down syndrome or chromosomal abnormalities like Edwards Syndrome or Patau Syndrome.
The cells in our body consist of many parts including the nucleus. The genetic matter is contained in the nucleus. Generally, the nucleus has 23 pairs of chromosomes and they are inherited from the mother and the father.
However, people born with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21. This is not a curable condition and results in delays in the development of the child and also develops physical characteristics separate from the normal kids.
Some of the characteristics include:
-
Short stature
-
Low muscle tone
-
Eyes with an upward slant
This condition has been found in one in 700 babies and is among the most common genetic problems affecting babies.
Edwards syndrome and Patau syndrome are rare and fatal chromosomal abnormalities. If a child is born with either of the two conditions, they die in the first year.
Advantages of conducting NT scan
There are several benefits associated with conducting the NT scan normal report when a woman is pregnant. Some of the benefits are as follows:
-
Chromosomal abnormalities (Edward’s syndrome or Patau syndrome), genetic problems, congenital heart abnormalities, risk of miscarriages, and chances of developing Down syndrome can be detected early in the pregnancy. This is the biggest benefit that one can get from the NT scan.
-
If the screening shows that there is a risk for the baby, one can perform other tests. It helps in deciding whether to keep the child or not. The gynecologist can give better guidance in such situations.
-
Since this is a non-invasive test, this must be performed beforehand on a pregnant woman before invasive tests are conducted. Invasive tests are risky and often carry the risk of miscarriages.
-
Like the other scans done during pregnancy, this test also gives great feedback about the health of the child in the womb of the mother. The NT scan shows the child in an extremely detailed manner. It confirms the due date of the child as well.
When must an NT scan be done during pregnancy?
The clear space at the unborn child’s back disappears by week 15. This is the reason why an NT scan report is conducted in the first trimester of pregnancy. The test also consists of blood tests for checking the plasma protein and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). It is a maternal hormone. Any abnormal level in either is indicative of a chromosome problem.
Who must get an NT scan?
The NT scan is recommended for most pregnant women. It is among the most common prenatal tests conducted during the first trimester of pregnancy. Doing the test helps one to take important prenatal care decisions.
What is the working method of an NT scan?
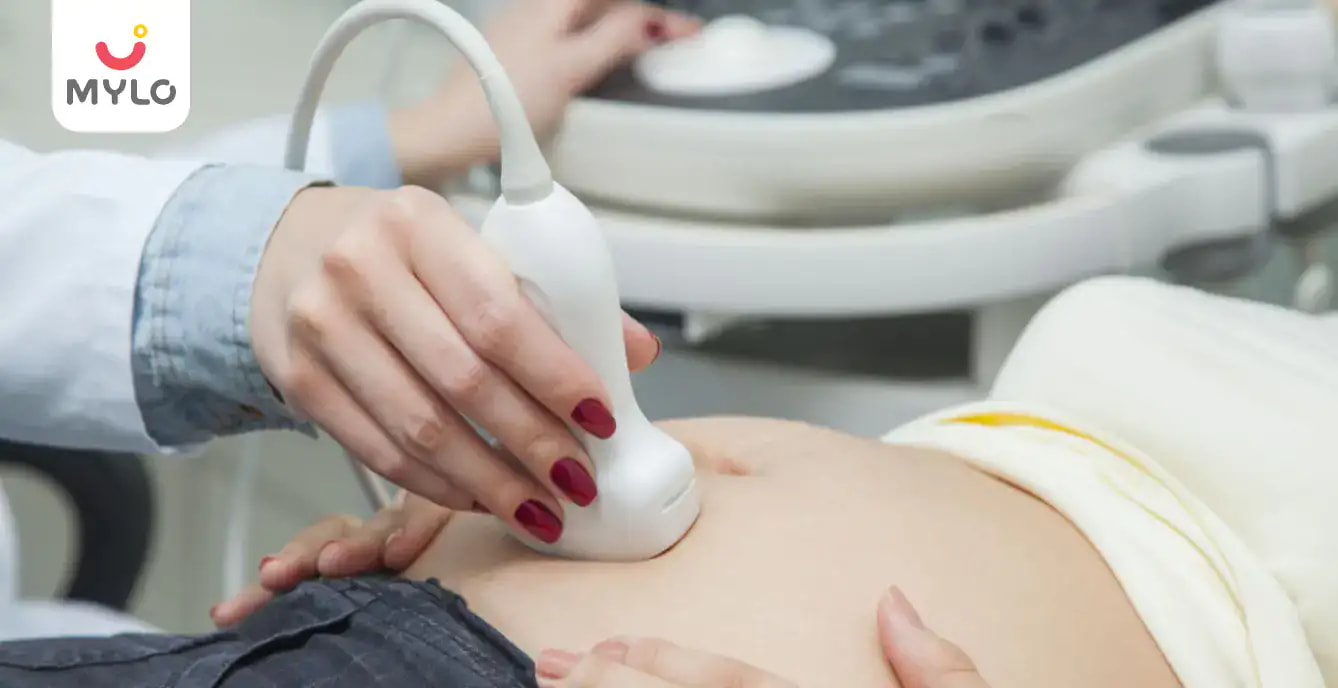
When the pregnant woman is screened, the doctor conducts an abdominal ultrasound to get the NT scan report sample. One can do a transvaginal test alternatively. In that test, the ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina of the woman.
High-frequency sound waves are used in the ultrasound for creating an image from inside the body of the pregnant woman. With the help of this image, the doctor will be able to measure the translucency or clear space at the neck of the unborn child. Then the age of the woman is entered in a computer program for calculating the risk of the baby and the chances of it developing any abnormality.
The NT scan cannot completely diagnose whether the child has Down Syndrome or other chromosomal problems. It can only indicate the chances of developing such abnormalities. The pregnant woman must speak to the doctor for blood tests that will help to understand the risks that the child may have.
If an NT scan and blood tests are done on the pregnant woman, the screening becomes 85 percent correct in predicting Down Syndrome. Without conducting the blood test, the screening’s accuracy is at 75 percent.
What are the preparations to undertake for an NT scan?
There is no special preparation needed for undergoing an NT scan. The scan gets completed in half an hour. However, if the position of the child is not convenient, the doctor might ask the woman to wait before conducting the scan again. The maximum time the scan might take is an hour.
When the NT scan is conducted, the pregnant women lie down on the examination table and the technician moves the ultrasound wand over her stomach.
It is recommended that the woman drink water about an hour before conducting the test. A fuller bladder helps provide easier readings. The pregnant woman must wear comfortable clothing during the test as the ultrasound tech will be accessing the lower abdomen.
The results might be given to the woman on the day of the test itself. Or else the doctor might discuss the findings before one leaves the test center. One must remember that getting an abnormal result does not mean that the baby has a chromosomal problem. It is also true that getting normal results also does not ensure that the child will not have Down syndrome.
The test has a five percent false-positive rate. Five percent of pregnant women give birth to normal babies even after getting positive results. If the result is positive, then your doctor might suggest another blood test known as prenatal cell-free DNA screening. It helps to examine the fetal DNA in the blood and helps access the risk of the baby for Down syndrome and other disorders.
What do the levels in Nuchal Translucency indicate?
Nuchal Translucency level that is less than 3.5mm is the normal range. The doctors usually rule out Down Syndrome if the test result comes within 2.5mm and 3.5 mm. Any increase in the NT levels may be suggestive of chromosomal abnormalities in children.
If the NT level of the baby is 6mm, it shows that there is a greater risk of chromosomal abnormalities. However, it occurs very rarely in babies.
Diagnostic testing vs screening?
NT scan normal report images is a screening test and not a diagnostic test. Though pregnant women can be scared after getting positive results from the NT scan, they must remember that it is not a definitive conclusion. It just predicts the risk that the child might have.
There are major differences between diagnostic and screening testing. Screening tests help identify risk factors for an ailment. The diagnostic testing helps confirm the presence of a disease.
What are the steps to diagnosing an abnormality?
For diagnosing the chromosomal abnormalities, ask the doctor about the diagnostic testing. Aminocentesis is an option available for pregnant women. A needle is inserted through the abdomen into the amniotic sac for retrieving a fluid sample. This fluid consists of cells that provide important genetic details about the child.
Another diagnostic testing available is chorionic villus sampling. In this test, the doctor takes a sample of the tissue in the woman’s placenta and then they test it to check for chromosomal abnormalities and genetic disorders.
A word of caution- there is a small chance of miscarriage in both these tests.
Conclusion
NT scan is a non-invasive and safe test that does not cause harm to the pregnant woman or the unborn child. One must remember that first-trimester screening is recommended. However, this is an optional screening. You can opt or not opt for it. Many women skip such tests as they become anxious after knowing the results. It is best to talk with the gynecologist and share your anxieties and worries and how the results will affect your mental well-being.
Also read about: Fetal Doppler Scan During Pregnancy: In which week should you get it done?, Risks of Getting a Fetal Doppler Scan During Your Pregnancy, Second Trimester Fetal Anomaly Scan during Pregnancy: What does it detect?, Blood beta Hcg test: What is it, levels & How to read it?and Anomaly report
References
1. Healthwise Staff. (2022). First-Trimester Screening for Birth Defects. https://www.uofmhealth.org/
2. Berger A. (1999). What is fetal nuchal translucency?. NCBI
3. Healthwise Staff. (2022). Nuchal Translucency Screening Test. https://www.uofmhealth.org/



Written by
Neelam S
Get baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় আলুবোখরা: উপকারিতা ও ঝুঁকি | Prunes During Pregnancy: Benefits & Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় হিং | ঝুঁকি, সুবিধা এবং অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা | Hing During Pregnancy | Risks, Benefits & Other Treatments in Bengali
Women Specific Issues
স্তনের উপর সাদা দাগ: লক্ষণ, কারণ এবং চিকিৎসা | White Spots on Nipple: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় পোহা: উপকারিতা, ধরণ এবং রেসিপি | Poha During Pregnancy: Benefits, Types & Recipes in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় মাছ: উপকারিতা এবং ঝুঁকি | Fish In Pregnancy: Benefits and Risks in Bengali

Diet & Nutrition
গর্ভাবস্থায় রেড ওয়াইন: পার্শ্ব প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং নির্দেশিকা | Red Wine During Pregnancy: Side Effects & Guidelines in Bengali
- ইনার থাই চ্যাফিং: কারণ, উপসর্গ এবং চিকিৎসা | Inner Thigh Chafing: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment in Bengali
- গর্ভাবস্থায় ব্রাউন রাইস: উপকারিতা ও সতর্কতা | Brown Rice During Pregnancy: Benefits & Precautions in Bengali
- Velamentous Cord Insertion - Precautions, Results & Safety
- Unlock the Secret to Flawless Skin: 7 Must-Have Qualities in a Face Serum
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin: How Vitamin C Serum Can Transform Your Complexion
- Gender No Bar: 10 Reasons Why Everyone Needs a Body Lotion
- Unlock the Secret to Radiant Skin How to Choose the Perfect Body Lotion for Your Skin Type
- Top 10 Reasons to Apply a Body Lotion After Every Bath
- Communication in Toddlers: Milestones & Activities
- How to Improve Vocabulary for Toddlers?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Placenta Accreta
- Vulvovaginitis in Toddlers Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cerebral Palsy in Children
- Bitter Taste in Mouth During Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Remedies


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers |