Home

Conception

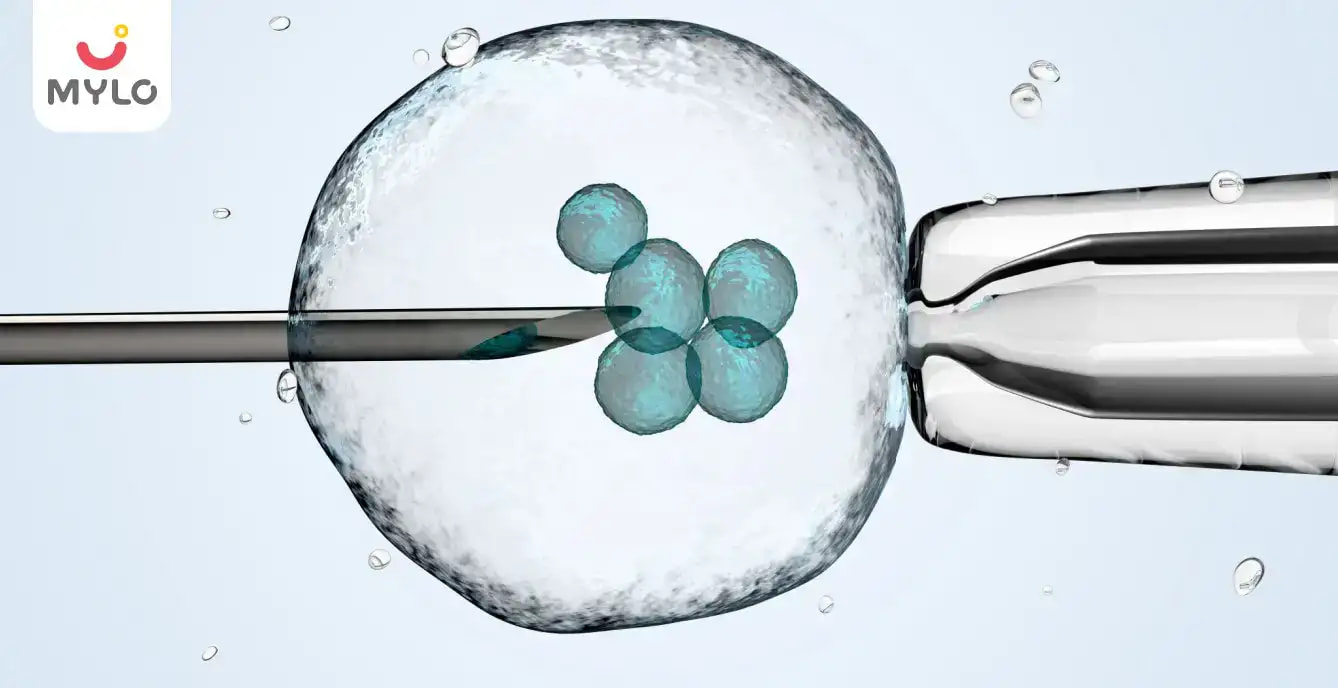
Embryo Freezing: Purpose & Outcome
In this Article

Conception
Embryo Freezing: Purpose & Outcome
Updated on 4 January 2023
The right time for having children is a concern for many of those who dream of parenthood. While for some, the right time may not occur until later in life, when fertility decreases naturally. Embryo freezing is a way in which couples can plan the time to have children. The best age to freeze embryo may vary for women and the key time to consider freezing eggs would depend on their life plans.
In this article, we will discuss why some people freeze embryo, the procedure of embryo freezing and the usage of frozen embryo, among more.
What is frozen embryo?
Embryo freezing, also known as embryo cryopreservation, is a process in which an embryo is frozen and stored for later use. Embryo freezing is a way to preserve a woman’s eggs to become pregnant at a later point in time. Frozen embryos are eggs that have been fertilised by a sperm, grown for several days and then frozen.
During the treatment, medication is used to increase the number of mature eggs available for harvesting. As the eggs mature, they are removed from a woman’s body, fertilised with sperm and kept as frozen embryos until she is ready for a child. People freeze embryo to assist with fertility and reproduction later. In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) can be used to ensure a successful pregnancy.
Why do people freeze embryos?
Embryo freezing mostly occurs after people opt for treatments like In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) to get pregnant. In these cases, there might be some good-quality embryos left that the couple may want to save in case the treatment doesn’t work or they want to try for another baby.
People who are undergoing hormone therapy, cancer treatment, gender transition surgery or any other medical intervention that may affect their fertility may also want to freeze embryo to preserve future fertility.
Are frozen embryos right for me?
The decision to freeze embryo is a personal choice. The cost of the procedure varies widely and your medical insurance may not cover fertility treatments. You must consider your goals, medical costs, ethical concerns and your partner’s preferences, among other considerations.
You may want to consider freezing your embryos if:
-
You wish to have the option of using your embryos in the future
-
You have to postpone your fertility treatment to a late date.
-
You have a medical condition or are undergoing medical treatment that may affect your fertility.
The effects of freezing embryos
Embryo freezing can help people have a baby later in life. When frozen embryos are needed later in life, a fertility specialist will use the embryos as desired and transfer them to the woman’s uterus. Freezing embryos doesn’t pose risks like congenital disabilities, premature birth, low birth weight or fetal health problems to the resulting pregnancy.
How does the usage of embryos trigger pregnancy?
The frozen embryos are transferred to the woman’s uterus, also known as frozen embryo transfer (FET). When the prospective mother’s uterus is ready for the transfer, the doctor inserts a catheter through the vagina and into the cervix and into the uterus to inject the embryo. The embryo is transferred into the uterus usually five days after ovulation. Ten days after the embryo transfer, a blood pregnancy test can help confirm if the procedure was successful and resulted in pregnancy.
How long can I keep my embryos in storage before using them in treatment?
You can freeze embryo and store the frozen embryos for up to 10 years before using them in fertility treatment. The frozen embryos are not compromised in quality and remain good for use even after years of being stored.
How much control do I have over what happens to my embryos?
Before the embryo freezing procedure is carried out, you’ll be required to sign relevant consent forms which will state the terms for future use. The consent form will determine how long you want the embryos to be stored, what happens to the frozen embryos if you were to die or become unable to make decisions, whether the frozen embryos can be donated for someone else’s treatment and any other conditions for the use of the frozen embryos.
How should I get ready for freezing embryos?
Before starting a cycle for retrieving eggs to create embryos, your doctor will check your hormone levels and perform an ultrasound to make sure your ovaries are ready for the procedure. You will then be given injectable medications to stimulate the ovaries to grow multiple follicles, where the eggs grow and can easily be harvested from.
What happens if I don't renew my storage consent at the proper time?
In case, you don’t renew your consent to store your frozen embryos at the right time, they will be removed from storage and disposed of. Your clinic or storage facility might ask you before disposing of the frozen eggs.
Keep your contact information up to date
It’s important to keep your contact information updated with the clinic so that they can inform you about your consent to storage or if it needs to be renewed. If the clinic is unable to contact you or obtain your consent for storage renewal, then your frozen embryos will be removed from storage and disposed of.
What if one of us decides not to use or donate embryos?
You, your partner or the donor can withdraw or change their consent at any time before using the frozen embryos. If you or your partner withdraw their consent, then the frozen embryos can no longer be used in treatment. If one person withdraws the consent, there might be a cooling-off period of up to a year. If you or your partner still don’t want the embryos, then they will be removed from storage.
How risk-free are treatments utilizing frozen embryos?
Treatments that utilise frozen embryos such as IVF are risk-free and have been producing higher success rates each year. The success rates vary based on factors like the expecting parents’ health, the mother’s age at the time of retrieving eggs, the presence of any fertility issues and/or previous success or failure of fertility treatment and pregnancy.
Is freezing harmful to the embryos?
Embryo freezing may cause damage to the embryos. Thawing the frozen embryos may also damage them. If there are multiple frozen embryos, then some or all may not survive. Your doctor will inform you whether your embryos are suitable for freezing, thawing and implantation.
How much does freezing an embryo cost?
Embryo freezing involves several costs such as the initial hormone treatments, egg harvesting, fertility, embryo culture, freezing, storage and implantation. The egg retrieval and embryo freezing procedure can cost Rs. 50,000 to Rs. 1,00,000 in India. Some medical insurance covers assisted reproduction techniques including embryo freezing while others may not.
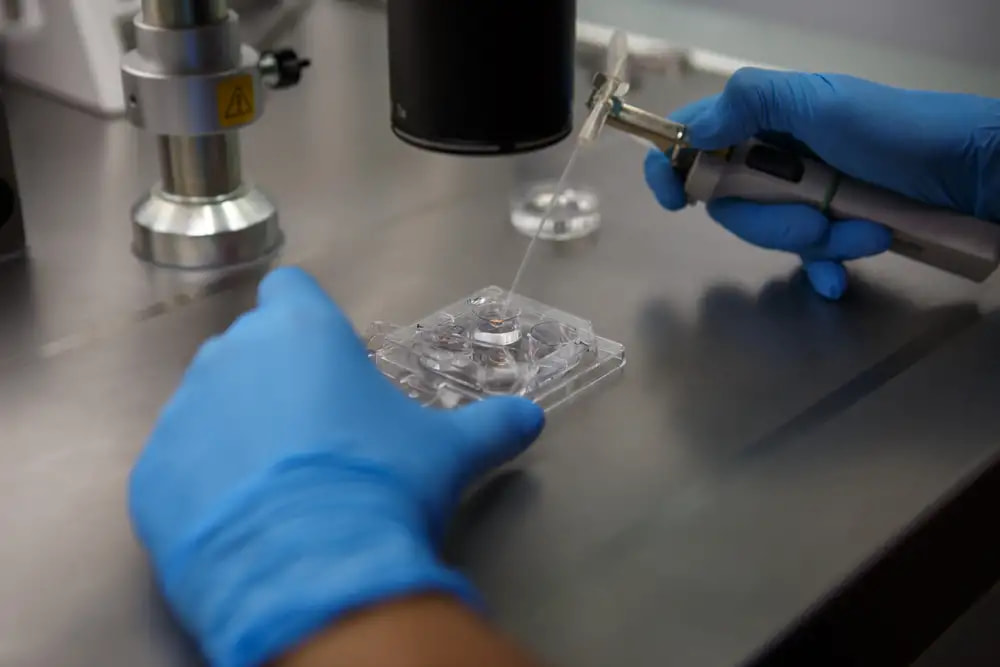
What takes place when embryos are freeze-dried (Embryo Cryopreservation)?
When the frozen embryos are needed later for use, a fertility specialist will:
-
Remove the frozen embryos from liquid nitrogen
-
Allow the embryos to return to normal temperature
-
Soak them to remove the cryoprotective agent (CPA)
-
Use the embryos as required, for example, transfer them into the uterus
What if I don't end up using every embryo I have during treatment?
If you don’t use your frozen embryos or there are some remaining after the treatment, you can:
-
Dispose of them
-
Donate them to someone else trying to have a baby
-
Donate them for research or educational purposes
If you are considering delaying family planning, you can opt for the embryo freezing procedure and preserve your fertility for the future.



Written by
Mylo Editor
Official account of Mylo Editor
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Questions
Hello frnds..still no pain...doctor said head fix nhi hua hai..bt vagina me pain hai aur back pain bhi... anyone having same issues??

Kon kon c chije aisi hai jo pregnancy mei gas acidity jalan karti hain... Koi btayega plz bcz mujhe aksar khane ke baad hi samagh aata hai ki is chij se gas acidity jalan ho gyi hai. Please share your knowledge

I am 13 week pregnancy. Anyone having Storione-xt tablet. It better to have morning or night ???

Hlo to be moms....i hv a query...in my 9.5 wk i feel body joint pain like in ankle, knee, wrist, shoulder, toes....pain intensity is high...i cnt sleep....what should i do pls help....cn i cosult my doc.

Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

General Mother
Exercises to Help Strengthen Weakened Pelvic Floor Muscles

Announcements & Celebrations
How Moms are Approaching 2023 - Mylo's Survey This Year End

Second Trimester
Second Trimester of Pregnancy

Third Trimester
Third Trimester of Pregnancy

Stretch Marks
Mylo Care Stretch Marks Cream Review

Breathlessness
How to Cure Breathlessness in Pregnancy Using 8 Natural Ways?
- Top 10 ways in which coconut water can help during pregnancy
- 7 Signs of Labor: Know What to Expect
- Points to Remember While Choosing Toys for Your Baby
- Top 10 Tips to Manage a Fussy Eater Toddler
- Baby Oral Care: When to Start Brushing Baby's Teeth
- Top 5 Supplements That You Need to Take During Pregnancy
- Reasons To Stop Working During Pregnancy
- Aspirin in Pregnancy : Can It Harm You or Your Baby?
- Top 10 Most Popular Bollywood Movies of 2022
- Infections During Pregnancy That Can Harm Your Baby
- Top tips: Travelling with a 2-year-old
- Pregnancy Insomnia: Meaning & Causes
- Follow These 6 Labor Tips and Rock Your First Birth
- What is the Importance of Baby Kick Counting During Pregnancy?


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN
















- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers |