Home

Sex Life

Trichomoniasis: Meaning, Symptoms, Causes and Risks
In this Article

Sex Life
Trichomoniasis: Meaning, Symptoms, Causes and Risks
Updated on 7 July 2023
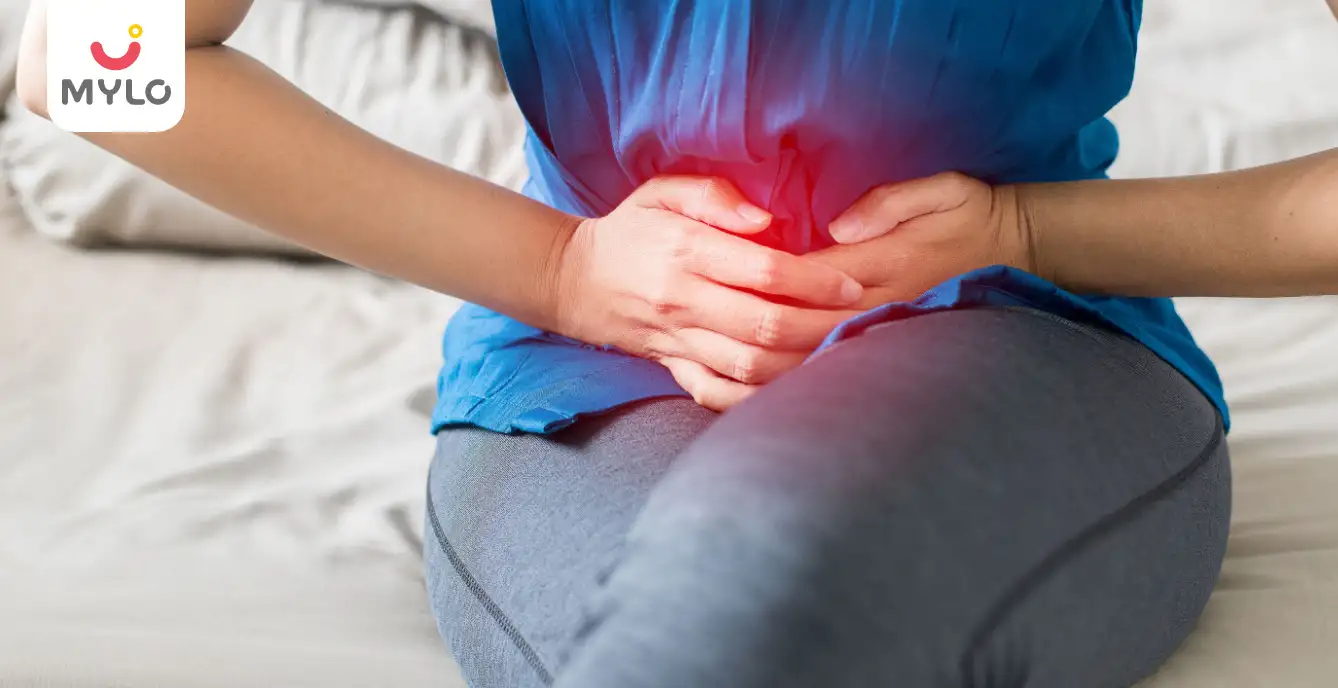
Trichomoniasis, also known as “trich,” is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. This infection is one of the most common curable STIs worldwide, affecting an estimated 156 million people every year, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In this article, we’ll explore the meaning, symptoms, causes, and risks associated with trichomoniasis.
What is Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is an STI caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, which can infect both men and women. This infection is transmitted through sexual contact with someone who has the parasite, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. The infection can also be spread through sharing sex toys, although this is less common.
Once a person is infected with trichomoniasis, they may experience symptoms ranging from mild to severe, or they may not have any symptoms at all.
Trichomoniasis Symptoms
Symptoms of trichomoniasis can vary depending on the severity of the infection and whether the person infected is male or female. Symptoms of Trichomoniasis are as follows:
1. Vaginal discharge
Women may experience a frothy, greenish-yellow discharge from the vagina.
2. Itching or burning
Both men and women may experience itching, burning, or irritation in the genital area.
3. Pain during urination
Men may experience pain or discomfort during urination.
4. Pain during sex
Women may experience discomfort or pain during sex.
5. Foul odor
Both men and women may notice a foul odor coming from the genitals.
6. Swelling or redness
Women may experience swelling or redness of the genitals.
You may also like: Burning Sensation After Sex: What Could It Mean
7. Lower abdominal pain
Women may experience lower abdominal pain, which can be a sign of a more severe infection.
Causes of Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, which is transmitted through sexual contact with someone who has the parasite. This can include vaginal, anal, or oral sex, as well as sharing sex toys. The parasite can survive outside of the body for a short period of time, which means it can be transmitted through objects like towels, wet clothing, or toilet seats, although this is less common.
The risk of contracting trichomoniasis is higher for people who have multiple sexual partners, those who have unprotected sex, and those who have a history of STIs. Women who are pregnant may also be at a higher risk of contracting trichomoniasis, as the infection can lead to complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
You may also like: Infections During Pregnancy That Can Harm Your Baby
What are the Risks of Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis can lead to a several health complications if left untreated, including:
1. Increased risk of HIV
People who are infected with trichomoniasis are more likely to contract HIV if they are exposed to the virus.
2. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
PID is a serious infection of the female reproductive system that can cause long-term health problems, including infertility. Trichomoniasis is a risk factor for developing PID.
3. Preterm birth
Pregnant women with trichomoniasis are at higher risk of delivering their baby prematurely, which can lead to a range of health problems for the baby.
4. Prostate problems
Men with trichomoniasis may experience inflammation of the prostate gland, which can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty urinating.
5. Increased risk of cervical cancer
While trichomoniasis does not cause cervical cancer directly, it can cause inflammation that may increase the risk of developing cancer over time.
6. Decreased sexual pleasure
In some cases, trichomoniasis can cause discomfort or pain during sex, which can decrease sexual pleasure and lead to sexual problems.
How is Trichomonas Infection Identified?
It's important to get tested for trichomoniasis and other STIs regularly, especially if you are sexually active. Trichomonas infection is identified through several methods, including physical examination, laboratory testing, and differential diagnosis.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will examine the genitals and look for signs of inflammation, discharge, and other symptoms. In women, a pelvic exam may be performed to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive system.
Laboratory Testing
Laboratory testing is the most reliable method of diagnosing trichomonas infection. The following tests may be used:
1. Microscopic examination: A sample of vaginal or urethral discharge is taken and examined under a microscope to look for the presence of Trichomonas vaginalis.
2. Nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT): This test detects the genetic material of the parasite and is highly sensitive and specific.
Differential Diagnosis
Other conditions may cause symptoms similar to trichomonas infection, and a differential diagnosis is essential to rule out other possible causes. Some conditions that may be considered during differential diagnosis include:
1. Yeast infection: Yeast infections can cause vaginal discharge, itching, and pain during sex.
2. Bacterial vaginosis: Bacterial vaginosis is a bacterial infection that can cause vaginal discharge and odor.
3. Gonorrhea and chlamydia: These are bacterial STIs that can cause similar symptoms to trichomonas infection.
4. Genital herpes: Genital herpes can cause painful blisters and sores in the genital area.
5. Urinary tract infection: Urinary tract infections can cause painful urination, frequent urination, and lower abdominal pain.
How to Prevent Trichomonas Infection?
Here are some ways to prevent the infection:
1. Abstinence
The most effective way to prevent trichomoniasis and other sexually transmitted infections is to abstain from sexual activity.
2. Mutual monogamy
If you are sexually active, having sex with only one partner can help reduce the risk of infection.
3. Use of condoms
Using condoms during sexual activity can help reduce the risk of trichomoniasis and other STIs.
4. Regular testing
Getting tested for trichomoniasis and other STIs regularly, to detect infections early and prevent the spread of infection.
5. Avoid sharing personal items
Sharing personal items such as towels, underclothing, and sex toys can increase the risk of transmitting trichomoniasis and other STIs.
6. Practicing good hygiene
Practicing good hygiene, including washing the genital area before and after sexual activity, can help reduce the risk of trichomoniasis and other STIs.
You may also like: How to Clean Your Vagina & Vulva | Complete Guide
Trichomonas Infection Treatment
If you or your partner is diagnosed with trichomoniasis or any other STI, it's essential to seek medical treatment as soon as possible and complete the full course of medication prescribed by your healthcare provider.
The primary treatment option for Trichomoniasis is the use of oral antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for Trichomoniasis are metronidazole and tinidazole. These medications are effective in eliminating the infection caused by the Trichomonas parasite. The standard treatment usually involves a single dose of the antibiotic. However, in some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend a longer course of treatment or additional doses depending on the severity of the infection.
It is important for both the infected individual and their sexual partner(s) to undergo treatment simultaneously to prevent reinfection. Healthcare providers may also advise abstaining from sexual activity until both partners have completed the treatment. If an individual is allergic to or cannot tolerate metronidazole or tinidazole, alternative treatment options can be considered. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or an allergy specialist in such cases.
Retesting for Trichomoniasis is recommended approximately three months after completing the treatment to ensure that the infection has been successfully cleared. In cases of recurrent or persistent infections, additional treatment options and drug susceptibility testing can be explored in consultation with healthcare providers or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted infection that affects millions of people worldwide. The main mode of transmission for trichomoniasis is through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Prevention is key when it comes to trichomoniasis. By practicing safe sex, getting regular screenings for sexually transmitted infections, and maintaining open communication with sexual partners, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting and spreading this infection.
References
1. Kissinger P. (2015). Trichomonas vaginalis: a review of epidemiologic, clinical and treatment issues. BMC Infect Dis.
2. Schumann JA, Plasner S. (2022). Trichomoniasis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing



Written by
Madhavi Gupta
Dr. Madhavi Gupta is an accomplished Ayurvedic doctor specializing in Medical content writing with an experience of over 10 years.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles
Pregnancy Journey
Gallstones in Pregnancy: Symptoms, Complications & Treatment

Fertility
Fertility Massage: A Holistic Approach to Boosting Fertility Your Chances of Conception

Care for Baby
Baby Vomiting After Feeding: Understanding the Causes and Solutions for Upset Stomach

Maternity Fashion
Why do you need to wear a high waisted panty during pregnancy?

IVF Pregnancy
Top 5 Precautions You Should Take After Getting an IVF Treatment

Baby Movements
Baby Kicking During Pregnancy: Unveiling the Wonders of Quickening in Pregnancy
- Daddy duties: Here's your guide to fatherhood
- Four-weeks old baby: Health, growth, care and more
- Baby cloth diapers by Mylo
- When to begin toilet training your child
- Are you a first time dad & scared? Here's some help
- Is your baby 3 months old now? Here's how to set-up a perfect sleep and feeding schedule for your little one?
- Painful Nipples During Breastfeeding: A Step-by-Step Approach for Managing Discomfort
- How to Manage and Alleviate Round Ligament Pain During Pregnancy?
- FSH LH Prolactin Test: What This Group of Tests Can Tell You About Your Fertility
- Why Berbitol is the Missing Piece in Your Supplement Stack
- Top 10 Action Movies to Watch on Netflix in 2023
- Foods to Avoid After Embryo Transfer & Other Precautions to Boost Your Chances
- Semen Analysis: A Comprehensive Look at Male Reproductive Health
- Understanding Premature Ejaculation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
Baby Carrier | Baby Soap | Baby Wipes | Stretch Marks Cream | Baby Cream | Baby Shampoo | Baby Massage Oil | Baby Hair Oil | Stretch Marks Oil | Baby Body Wash | Baby Powder | Baby Lotion | Diaper Rash Cream | Newborn Diapers | Teether | Baby Kajal | Baby Diapers Pants | Cloth Diapers | Laundry Detergent | Lactation Granules |








